Why Grout?
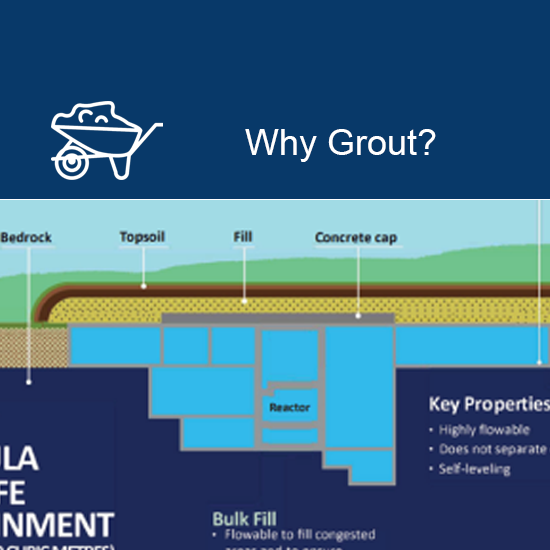
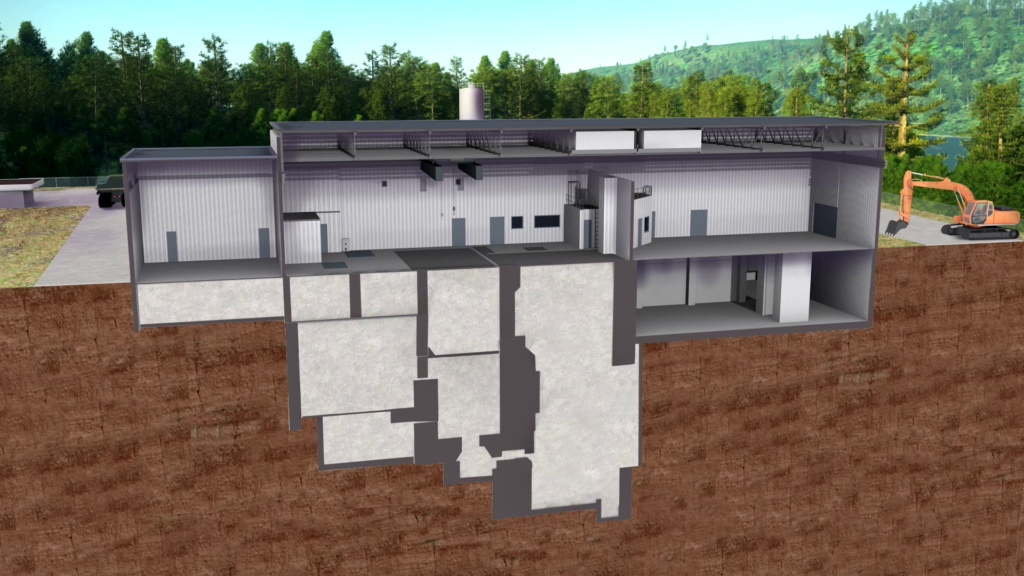
The below-grade areas of the NPD structure will be sealed with grout and concrete prepared at a temporary on site batch mixing plant.
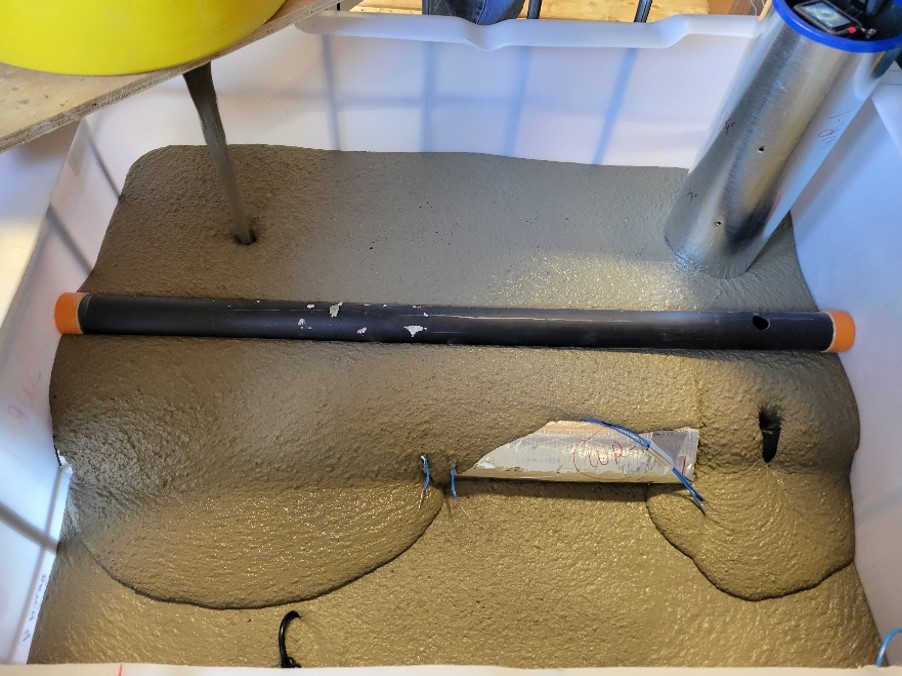
The grout developed for NPD is a mixture of cementitious materials (binder), sand, and water that produces a pourable, mortar-like, material that is pumped into the facility. Grout is used to help contain and isolate contaminants, ensure stability and slow the movement of groundwater entering the facility to reduce corrosion.
All above-grade structures will be demolished and placed into the below-grade structure as backfill prior to final grouting. The footprint above the reactor will be capped with reinforced concrete and the entire NPD facility will be covered with an engineered barrier. The ventilation stack will be retained to preserve the habitat of one of the largest known population of Chimney Swifts in Canada, and that are a species at risk. CNL will then restore the site by planting vegetation and prepare for long-term care and maintenance activities.
Through extensive research, CNL has developed a specially formulated grout, adapted to the unique requirements of the NPD facility. The test included fresh properties, such as determining the ability of the grout to flow around piping and tanks, and cured properties, such as strength and hydraulic conductivity, to determine how fast water can flow through it. Combined with the existing robust construction of the underground facility, the proposed grouting process will enhance protection of people and the environment.
CNL has added details on grout and grout formulations to the revised draft Environmental Impact Statement.
Learn More:
Watch how flowable grout works in an industrial setting